Mechanical • Laser • Backdrill • VIPPO
Comprehensive PCB Drilling & Interconnect Manufacturing
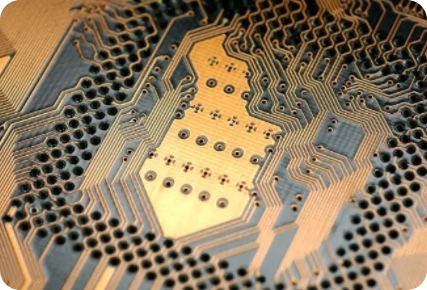
In the sophisticated realm of PCB fabrication, the drilling process serves as the critical intersection between mechanical precision and electrical performance. From standard through-holes to advanced HDI laser microvias and signal integrity backdrilling, we execute complex interconnects with micron-level tolerances.
Get an Instant Quote
Comprehensive PCB Drilling and Interconnect Manufacturing at APTPCB
In the sophisticated realm of printed circuit board (PCB) fabrication, the drilling process serves as the critical intersection between mechanical precision and electrical performance. It is the defining stage where layer-to-layer connectivity is established, signal paths are forged, and the thermal characteristics of the device are determined.
At APTPCB, we understand that our role goes beyond simply drilling holes. Prior to production, our MI engineers and CAM engineers, along with the CAM engineer QA team, thoroughly review your PCB files. We create and inspect the engineering documentation to ensure that everything aligns with the design intent. If any issues are found during this review, we provide feedback and suggest adjustments to the design before manufacturing begins. We do not simply replicate designs; we work collaboratively to ensure the design is optimized for manufacturing, avoiding potential issues that could arise during production.
Using advanced manufacturing technologies, we bring your complex interconnect architectures to life with absolute fidelity to your Gerber and ODB++ specifications. From standard rigid boards to high-density HDI rigid-flex platforms, our facility is equipped to handle the full spectrum of drilling requirements with micron-level tolerances.
Mechanical Drilling: The Foundation of Vertical Interconnection
For the vast majority of PCB designs, mechanical CNC drilling remains the backbone of manufacturing. We employ a fleet of high-speed, dynamic-depth-controlled spindles capable of processing thousands of hits per minute while maintaining strict positional accuracy relative to internal copper layers.
Through-Hole Conductivity and Isolation
The most fundamental unit of the PCB is the Through Hole. Its execution determines the board's long-term reliability.
- Plated Through Hole (PTH): This is the standard vertical interconnect. At APTPCB, we monitor our electroless and electrolytic copper plating lines to ensure the Via Barrel receives ductile, uniform coverage. This prevents barrel cracking during the thermal shock of assembly reflow.
- Non-Plated Through Hole (NPTH): Critical for electrical isolation and mounting. We strictly follow process routes that prevent plating deposition in these holes—either by drilling them after the plating cycle or by using tenting methods—ensuring the wall remains non-conductive.
- Mechanical Drill Hole: We handle a wide range of aspect ratios for standard signal and power transmission, ensuring the hole wall quality is smooth to facilitate reliable plating.
Component Interface and Assembly Tolerances
Different components require specific hole geometries to ensure proper soldering and mechanical fit. We adhere strictly to your fabrication drawings for:
- Component Lead Hole / Leaded Component Hole: Precision sizing for standard THT (Through-Hole Technology) devices.
- Pin-In-Hole / Pin Via: Manufactured to support Pin-in-Paste (intrusive reflow) processes, where hole volume is critical for solder paste calculations.
- Press-Fit Hole / Press-Fit Via: For solderless connectors, we execute Via for Press-Fit Connector designs. These require extremely tight tolerances (often +/- 0.05mm) and specific plating finishes (like immersion tin or silver) to create a cold-welded gas-tight interface without damaging the connector pin.
- Wire Via: Small diameter holes specifically designed for direct wire soldering.
Complex Shaping, Slots, and Routing
Modern PCBs often serve dual purposes as electrical circuits and mechanical structural elements. Our routing department is capable of producing complex internal cutouts:
- Plated Slot / Metalized Slot: Used extensively for high-current blade connectors or DC jacks. We ensure the plating is continuous around the slot radius.
- Through-Slot Metallized Hole: A variation where the slot acts as a grounded shielding element or mechanical guide.
- NPTH Slot / Long Slot: Typically used for high-voltage isolation (air gaps for creepage) or mechanical sliders.
- Geometric Versatility: We process designs containing Oval Hole, Oblong Hole, Rectangular Hole, and Square Hole features. For polarized connectors, we fabricate precise Key Slots.
Mechanical Integration Features
To support the final assembly of your product, we manufacture:
- Mounting Hole / Assembly Hole / Screw Hole: Standard non-plated holes for chassis attachment.
- Countersink Hole / Counterbore Hole: We utilize depth-controlled Z-axis drilling to create conical or flat-bottomed recesses, allowing screw heads to sit flush with or below the board surface.
- Chamfered Hole / Beveled Hole: We process holes with edge chamfers to prevent wire chafing or to facilitate easier pin insertion.
- Tooling Hole / Guide Hole / Pilot Hole: Essential for manufacturing alignment, these are maintained per your panelization drawing to secure the board during profiling and testing.
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) and Laser Architectures
As electronic devices shrink, the demand for routing density outpaces the physical limits of mechanical drilling. APTPCB employs state-of-the-art laser ablation technology to manufacture HDI boards that drive today's mobile and computing sectors.
Laser Process Capabilities
- Laser Drill Hole: We utilize advanced laser systems tailored to the material stack-up.
- CO2 Laser Via: Optimized for the rapid removal of dielectric materials (Prepreg, ABF, or RCC).
- UV Laser Via: Used for high-precision ablation of copper and dielectric, creating a clean Laser-Defined Hole with minimal carbonization or heat-affected zones.
- Hybrid Drill Hole (Laser + Mechanical): We possess the registration systems necessary to align mechanical through-holes with laser microvias on the same high-layer-count board.
Microvia Stacking and Topologies
We support all IPC-defined HDI types (Type I, II, III, and beyond) through advanced lamination cycles:
- Microvia / Ultra-Fine Microvia: Connecting adjacent layers with diameters often below 0.10mm (4 mil).
- Blind Via: A hole that connects an outer layer to an inner layer but does not penetrate the entire board.
- Buried Via: A via connecting internal layers only, fully encapsulated within the PCB structure.
- Buried Microvia: Laser vias located on internal cores.
- Blind & Buried Via: We manage complex sequential lamination to combine these technologies in a single stack-up.
Advanced Interconnect Structures
To maximize routing space, we offer sophisticated via architectures:
- Stacked Via / Stacked Microvia: Placing a laser via directly on top of a buried via or another microvia. This requires a planar surface, achieved through copper filling.
- Staggered Via / Staggered Microvia: Offsetting vias on subsequent layers, which provides better stress relief during thermal expansion.
- HDI Sequential Microvia: We manage the Sequential Build-Up (SBU) process to create multi-tiered interconnects.
- Skip Via: Laser vias that penetrate through two dielectric layers to connect Layer n to Layer n+2.
- Z-Axis Via: Specialized vertical interconnection methods for specific high-frequency laminates.
Via-in-Pad, Filling, and VIPPO Technology
The miniaturization of components like BGAs and QFNs often eliminates the space required for traditional Fanout Vias or Dogbone Via patterns. The solution is Via-in-Pad, and APTPCB offers the full suite of IPC-4761 plugging and filling processes to support this.
Via-in-Pad Configurations
- Via-in-Pad Open: The via is placed in the pad but left open. While low cost, this risks solder wicking.
- Via-in-Pad Plugged: Partially plugging the hole to restrict solder flow.
- Via-in-Pad Filled: Completely filling the via barrel with material.
- Via-in-Pad Capped / Capped Via: Plating over the filled via to restore a solderable surface.
- Via-in-Pad Plated Over (VIPPO): Also known as Via-in-Pad Filled and Capped. This is the premium standard for HDI. We drill, plate, fill the hole with epoxy, planarize the surface, and then cap-plate it. This creates a perfectly flat pad, essential for reliable soldering of Fine-Pitch Vias and BGA Escape Vias.
Material Science in Via Filling
We utilize specialized filling materials based on your design requirements:
- Resin-Filled Via / Epoxy-Filled Via: The standard non-conductive fill, matched to the CTE of the laminate to prevent expansion defects.
- Non-Conductive Filled Via: Ensures electrical insulation between the via walls and the surface cap.
- Conductive Filled Via: Historic use of silver/copper paste (less common now due to thermal mismatch).
- Copper-Filled Via: The microvia is completely filled with electroplated copper (Solid Copper Plating). This provides the ultimate electrical and thermal performance for stacked microvias.
- Epoxy Backfilled Via: Using resin to backfill controlled depth holes for surface smoothness.
Tenting and Protection
For vias not used in soldering pads, we offer various protection methods:
- Via Tenting / Tented Via: Covering the via with dry film solder mask.
- Solder Mask Plugged Via / Via Plugging: Forcing solder mask ink into the hole to seal it.
- Soldermask-Defined Plugged Via: Where the mask opening controls the plug geometry.
- Plugged & Capped Via: A hole plugged with resin and then capped with metal for hermeticity.
- Via Overprint: Applying solder mask over the plugged via to ensure complete insulation.
Signal Integrity: Backdrilling and Impedance Control
In the era of 5G, 112G PAM4, and PCIe Gen5, the physical structure of the via can degrade signal quality. APTPCB implements advanced drilling techniques to mitigate these effects.
Backdrilling (Stub Removal)
The unused portion of a plated through hole, known as the Via Stub, acts as a resonant antenna that causes signal reflection and insertion loss.
- Backdrill / Backdrilled Via: We perform a Controlled Depth Drilled Via operation from the secondary side to mechanically remove the copper stub.
- Stub Removal Drill: Our depth tolerance is precise, ensuring we remove the stub without damaging the active internal layers.
- Via Barrel Relief: We manage the transition zone to ensure clean signal paths.
High-Speed and RF Optimization
- Controlled Impedance Via / Impedance-Tuned Via: We manufacture vias with specific diameters and anti-pad clearances to match the transmission line characteristic impedance.
- High-Speed Via / Differential Pair Via: We ensure precise registration of drilled holes relative to the Anti-Pad Via Region and Return-Path Vias to maintain coupling.
- RF Via / Microwave Via: Fabricated with smooth walls and exact geometries for low-loss performance.
- Shielding Structures: We drill dense Via Fences, EMI Shield Fence Vias, Via Stitching, and Shielding Vias to create isolation barriers (Faraday cages) around sensitive RF blocks.
Thermal Management and Power Delivery
Heat is the primary enemy of reliability in power electronics. APTPCB manufacturing capabilities are integral to your thermal management strategy.
- Thermal Via / Thermal Via Array: We drill dense arrays intended to conduct heat from surface components to internal ground planes or bottom-side heatsinks.
- Heat Dissipation Via: Often enhanced with Copper-Filled Via technology or Heavy Copper Drill Hole processes to maximize thermal mass.
- Metal Core Via (MCPCB) / Thermal Through Hole (MCPCB): We are capable of drilling through aluminum or copper-based substrates for LED and automotive lighting, including Resin-Core Vias for electrical isolation.
- Power Via / Ground Via / High-Current Via: We optimize drilling and plating parameters to handle Thick-Copper Vias (up to 10oz or more), ensuring the barrel does not crack under high-current thermal loads.
- Copper-Dome Via / Copper-Capped Via: Specialized structures to enhance heat spreading on the surface.
Board Edge and Mechanical Fabrication
Your PCB is often part of a larger mechanical assembly. We provide specialized edge machining to facilitate system integration.
- Castellated Hole / Castellation: Also known as Half Hole or Plated Half Hole. We drill these on the panel border and perform a secondary routing pass to cut the hole in half. This creates a plated semi-cylinder, allowing the PCB to be surface-mounted as a module.
- Edge Plated Hole / Edge Via: We provide continuous plating wrapping around the board edge for chassis grounding or EMI shielding.
- Edge Slot / Via for Board-Edge Module: Creating slots or patterns for edge connectors.
- Via for Shield Can: Holes designed specifically to ground and retain metal RF shields (cans).
Quality Assurance, Testing, and Reliability
A drilled hole is only as good as its verification. We integrate drilling into a holistic quality control ecosystem.
Testing and Verification
- Test Via / Test Hole / Probe Via: We preserve these specific locations for electrical connectivity testing.
- ICT Test Hole (In-Circuit Test) / Flying-Probe Via: We ensure these pads remain unmasked and clean for test probe contact.
- Fiducial Hole / Alignment Hole / Registration Hole: We drill these to verify layer-to-layer alignment and for use in automated assembly optical inspection.
Reliability Processes
- Cross-Section Analysis: We regularly destroy sample coupons to inspect the Via Barrel integrity, measuring plating thickness and checking for cracks or voids.
- Desmear: We use Plasma-Prepared Hole cycles to remove drill smear (melted resin) from the hole wall, ensuring perfect interconnection between the barrel and internal copper layers.
- Moisture Management: For flex and rigid-flex designs, we fabricate Moisture Relief Holes, Vent Holes, Gas Relief Holes, and Vacuum Relief Holes to allow trapped volatiles to escape during high-temperature reflow, preventing delamination.
- Solder Thieving Hole: We support designs incorporating these in wave solder pallets to prevent solder bridging.
- Deep Drilled Hole / Multi-Depth Drill / Step-Drilled Hole: We have the Z-axis control to execute holes that stop at precise depths for blind mechanical assembly.
- Non-Functional Pad Via: We can remove or keep non-functional pads based on your signal integrity netlist requirements.
- Cavity Via / Embedded Via: Supporting component embedding technologies.
At APTPCB, we combine these extensive drilling capabilities with a rigid adherence to quality standards. Whether your project requires a simple mounting hole or a complex multi-lamination HDI stack with backdrilled connectors, our team is ready to execute your design with precision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Answers to the questions we hear most from hardware teams.
How do you handle PTH, NPTH, and press-fit requirements?
We follow your fabrication drawings to size PTH/NPTH, pin-in-hole, and press-fit holes, control plating or isolation paths, and hold tight tolerances with depth-controlled drilling where needed.
What laser and HDI via structures are supported?
CO2 and UV laser microvias, blind/buried vias, stacked or staggered HDI microvias, skip vias, and hybrid mechanical/laser registrations across sequential build-up cycles.
Do you offer via-in-pad and filling processes?
Yes—open, plugged, filled, capped, and VIPPO via-in-pad options with resin, epoxy, copper, or mask plugging per IPC-4761 to achieve flat, solderable pads.
Can you support backdrilling for high-speed signals?
We perform controlled-depth backdrill stub removal with precise depth tolerance to clean up signal paths and minimize reflections on high-speed or RF nets.
How do you address thermal and mechanical requirements?
Thermal vias, heat-dissipation and metal-core drills, edge plating and castellations, moisture-relief holes, and mechanical slots or countersinks are produced to your specs with QA checks like cross-section and desmear control.
PCB drilling & backdrill review
Send stackup, drill files, impedance targets, and via strategy—we return a drill stack, tolerances, and backdrill plan.